Features Deep Dive
A comprehensive exploration of Product-FARM’s enterprise-grade capabilities, designed for scalability, reliability, and exceptional developer experience.
Template & Cloning System
Product-FARM’s template and cloning system enables rapid product development while maintaining data integrity and preventing unauthorized modifications.
What Are Templates?
Templates are reusable product configurations that define:
- Product structure - Components, attributes, and relationships
- Dynamic enumerations - Template-specific value sets
- Template types - Category classification (e.g., “insurance”, “finance”, “retail”)
- Base configurations - Default rules and attribute values
Templates serve as blueprints for creating new products quickly while ensuring consistency across your product catalog.
Deep Clone vs Selective Clone
Product-FARM supports two cloning strategies:
Deep Clone
- Creates a complete copy of the entire product
- Generates new unique IDs for all entities
- Preserves all relationships and dependencies
- Ideal for creating product variants or testing environments
POST /api/products/{id}/clone
{
"newProductId": "auto-insurance-premium-v2",
"newProductName": "Auto Insurance Premium V2"
}
Selective Clone
- Filter what gets cloned using
CloneSelections - Choose specific components, datatypes, enumerations, or functionalities
- Reduce clone size and complexity
- Perfect for partial product derivation
POST /api/products/{id}/clone
{
"newProductId": "auto-insurance-basic",
"newProductName": "Auto Insurance Basic",
"selections": {
"componentIds": ["core", "pricing"],
"excludeFunctionalities": ["advanced-analytics"]
}
}
DoS Prevention Limits
To protect system stability, cloning operations enforce these limits:
| Entity Type | Maximum per Clone |
|---|---|
| Abstract Attributes | 10,000 |
| Concrete Attributes | 100,000 |
| Rules | 10,000 |
| Functionalities | 1,000 |
Performance Caching System
Product-FARM implements a sophisticated caching layer to achieve sub-microsecond evaluation times.
LRU Cache Architecture
The caching system uses a Least Recently Used (LRU) eviction policy with:
- Write-through caching - Writes go to both cache and database
- Bounded memory usage - Fixed cache sizes prevent memory exhaustion
- Automatic eviction - Oldest entries removed when cache is full
- Cache warming - Frequently accessed data preloaded on startup
Configurable Cache Sizes
| Cache Type | Default Size | Maximum |
|---|---|---|
| Products | 100 | 1,000 |
| Attributes | 10,000 | 100,000 |
| Rules | 10,000 | 100,000 |
| Compiled Rules | 10,000 | 100,000 |
Configure cache sizes in your deployment configuration:
cache:
products:
size: 500
attributes:
size: 50000
rules:
size: 50000
compiled_rules:
size: 50000
Performance Impact
| Scenario | Without Cache | With Cache | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Product Load | ~5ms | ~50μs | 100x |
| Rule Evaluation | ~1.15μs | ~330ns | 3.5x |
| Attribute Lookup | ~500μs | ~10μs | 50x |
Tiered Compilation Engine
Product-FARM uses a tiered compilation strategy inspired by JIT compilers to optimize rule evaluation.
Tier 0: AST Interpretation
Initial rule execution uses Abstract Syntax Tree (AST) interpretation:
- Immediate execution - No compilation overhead
- Evaluation time - ~1.15μs per rule
- Memory efficient - Minimal memory footprint
- Debug-friendly - Easy to trace and debug
Best for:
- Rules executed infrequently
- Development and testing
- Initial rule validation
Tier 1: Bytecode Compilation
Hot rules are automatically promoted to bytecode execution:
- Compiled execution - Optimized bytecode VM
- Evaluation time - ~330ns per rule
- 3.5x speedup - Significant performance improvement
- Cached - Compiled bytecode stored in cache
Best for:
- Frequently executed rules
- Production workloads
- High-throughput scenarios
When Promotion Occurs
Rules are promoted to Tier 1 based on:
- Execution count - After N executions (configurable)
- Time threshold - Rules accessed within a time window
- Explicit promotion - API-triggered compilation
- Batch compilation - Compile all rules on product activation
// Compilation threshold configuration
compilation:
promotion_threshold: 100 // Promote after 100 executions
time_window: 60s // Consider executions in last 60 seconds
eager_compile: false // Compile all rules immediately
DAG Execution Engine
The Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) execution engine automatically manages rule dependencies and enables parallel execution.
Dependency Detection
The engine analyzes each rule to detect:
- Input variables - Variables read by the rule
- Output variables - Variables written by the rule
- Implicit dependencies - Inferred from expression analysis
{
"rule_id": "calculate_premium",
"inputs": ["base_rate", "age_factor", "risk_score"],
"outputs": ["final_premium"],
"dependencies": ["calculate_age_factor", "calculate_risk_score"]
}
Level Assignment Algorithm
Rules are assigned to execution levels using topological sort:
- Level 0 - Rules with no dependencies (inputs only)
- Level 1 - Rules depending only on Level 0 outputs
- Level N - Rules depending on Level N-1 outputs
flowchart TB
subgraph L0["⚡ Level 0 - Parallel"]
direction LR
R0_1["get_age"]
R0_2["get_income"]
R0_3["get_credit_score"]
end
subgraph L1["🔗 Level 1"]
direction LR
R1_1["calculate_age_factor"]
R1_2["calculate_income_ratio"]
end
subgraph L2["🔗 Level 2"]
R2_1["calculate_risk_score"]
end
subgraph L3["🔗 Level 3"]
R3_1["calculate_final_premium"]
end
R0_1 --> R1_1
R0_2 --> R1_2
R0_3 --> R2_1
R1_1 --> R2_1
R1_2 --> R2_1
R2_1 --> R3_1
style L0 fill:#065f46,stroke:#10b981,color:#fff
style L1 fill:#1e3a5f,stroke:#3b82f6,color:#fff
style L2 fill:#4c1d95,stroke:#8b5cf6,color:#fff
style L3 fill:#6366f1,stroke:#8b5cf6,color:#fff
Parallel Execution Strategy
Rules within the same level execute in parallel:
- Thread pool - Configurable worker threads
- Work stealing - Efficient load balancing
- Level synchronization - Wait for level completion before next
- Result aggregation - Collect outputs for next level
Throughput comparison:
| Mode | Throughput |
|---|---|
| Sequential (AST) | 870K evals/sec |
| Sequential (Bytecode) | 3M evals/sec |
| Parallel (AST) | 6.5M evals/sec |
| Parallel (Bytecode) | 22M evals/sec |
Cycle Detection
The engine prevents circular dependencies:
- Build-time validation - Detect cycles when rules are created
- Runtime verification - Double-check before execution
- Clear error messages - Identify which rules form the cycle
{
"error": "CYCLE_DETECTED",
"message": "Circular dependency detected",
"cycle": ["rule_a", "rule_b", "rule_c", "rule_a"]
}
RBAC & Security
Product-FARM provides fine-grained access control at multiple levels.
Component-Level Permissions
Control access at the component level:
- Read - View component attributes and rules
- Write - Modify attributes and rules
- Delete - Remove attributes and rules
- Admin - Full control including permissions
{
"component_id": "pricing",
"permissions": {
"pricing-team": ["read", "write"],
"analysts": ["read"],
"admins": ["read", "write", "delete", "admin"]
}
}
Template Immutability Control
Mark templates as immutable to prevent modifications:
- Full immutability - No changes allowed
- Partial immutability - Specific fields locked
- Time-based locks - Immutable after activation
- Override capability - Admin-only changes
Product Lifecycle Permissions
Control who can transition products between states:
| State Transition | Required Permission |
|---|---|
| Draft → Pending Approval | submit |
| Pending Approval → Active | approve |
| Active → Discontinued | discontinue |
| Any → Draft (clone) | clone |
Approval Workflows
Configure multi-step approval processes:
- Submission - Product owner submits for review
- Technical Review - Engineering validates rules
- Business Review - Business approves logic
- Activation - Final approval and go-live
approval_workflow:
stages:
- name: technical_review
approvers: ["engineering"]
required: 1
- name: business_review
approvers: ["product", "compliance"]
required: 2
- name: final_approval
approvers: ["leadership"]
required: 1
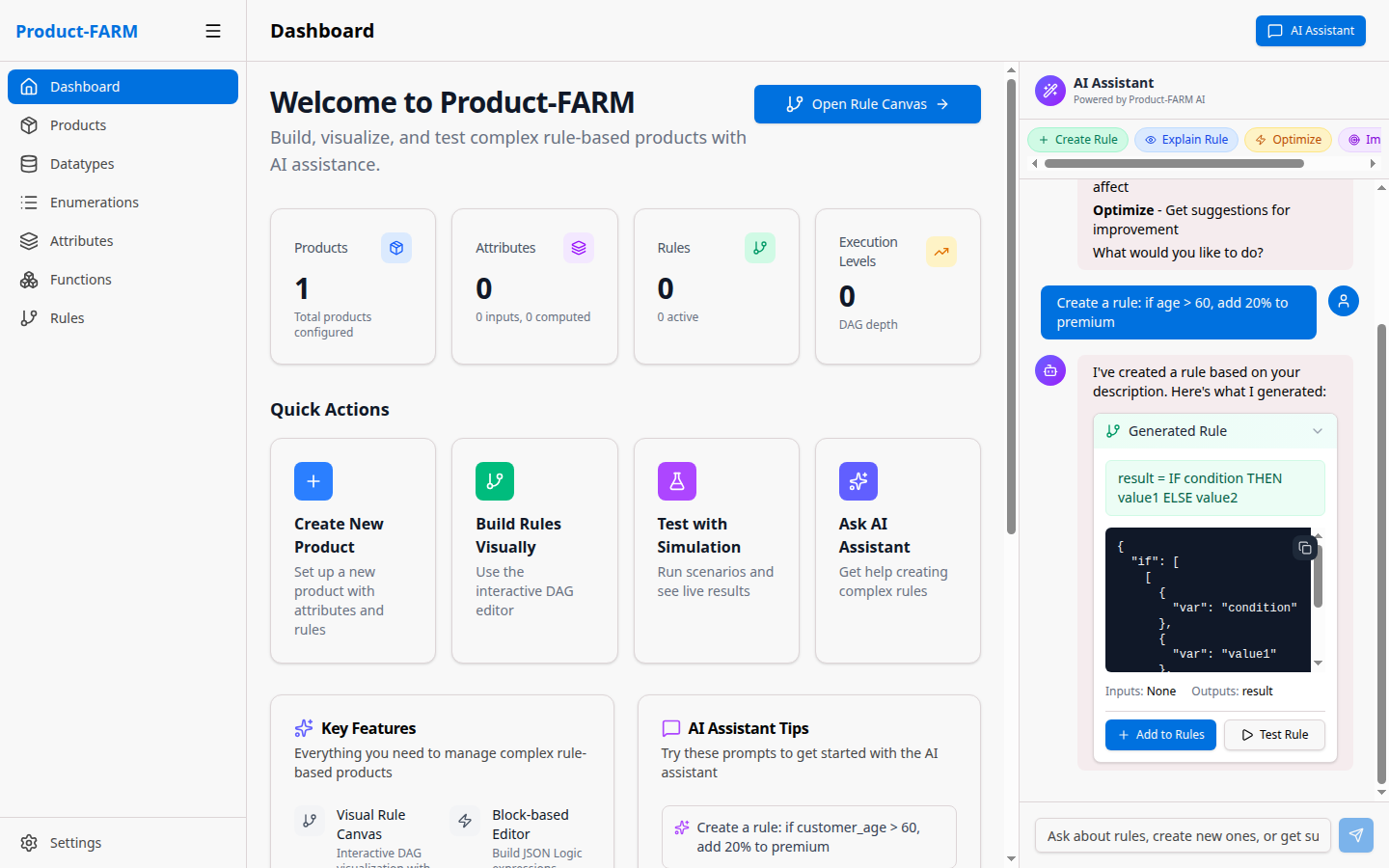
AI-Powered Assistance
Product-FARM includes an intelligent AI assistant that transforms how you create, understand, and optimize business rules.
Natural Language Rule Creation
Describe your rules in plain English, and the AI generates complete, executable rule definitions:
Example Interaction:
You: "Create a rule: if age > 60, add 20% to premium"
AI: I've created a rule based on your description. Here's what I generated:
Name: apply_age_premium
Expression: IF age > 60 THEN premium * 1.2 ELSE premium
Inputs: [age, premium]
Outputs: [adjusted_premium]
The AI understands:
- Conditional logic - If/then/else statements
- Mathematical operations - Percentages, multiplications, additions
- Business terminology - Premium, discount, rate, factor
- Complex conditions - AND/OR combinations, nested logic
Rule Explanation
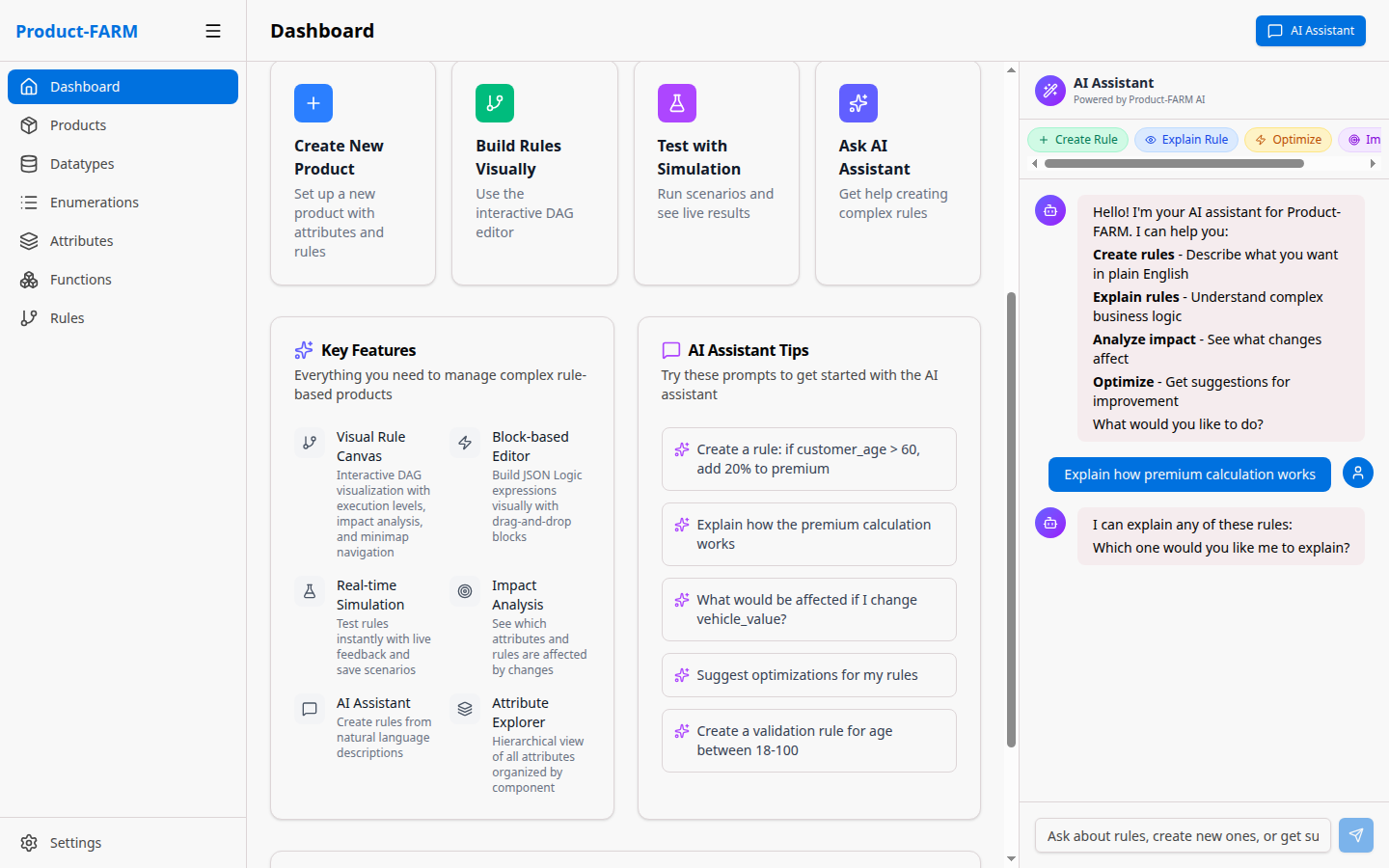
Have the AI explain complex rule logic in plain English:
You: "Explain how premium calculation works"
AI: The premium calculation follows these steps:
1. Base premium is determined by coverage amount ($10 per $1,000)
2. Age factor is applied:
- Under 30: 0.9x (10% discount)
- 30-50: 1.0x (standard rate)
- Over 50: 1.2x (20% increase)
3. Smoker status adds 30% if applicable
4. Final premium = base × age_factor × smoker_factor
Features:
- Step-by-step breakdowns - Understand execution flow
- Dependency visualization - See how rules connect
- Input/output mapping - Know what each rule needs and produces
Impact Analysis
Before making changes, understand what will be affected:
You: "What would be affected if I change vehicle_value?"
AI: Changing vehicle_value would impact:
Direct Dependencies:
├── calculate_collision_premium (uses vehicle_value directly)
├── calculate_comprehensive_premium (uses vehicle_value directly)
└── determine_deductible_options (based on value ranges)
Downstream Effects:
├── total_premium (sum of all premiums)
├── monthly_payment (derived from total_premium)
└── quote_display (formats final values)
Functionalities Affected:
├── generate_quote
└── calculate_renewal
Optimization Suggestions
Get AI-powered recommendations to improve your rules:
You: "Suggest improvements for my rules"
AI: I've analyzed your rules and found opportunities:
🚀 Performance Optimizations:
- Rules "check_age" and "check_income" can be combined
- "calculate_factor" runs twice with same inputs - consider caching
📋 Maintainability:
- "rule_123" has no description - add documentation
- 3 rules have similar logic - consider extracting common pattern
⚠️ Potential Issues:
- "discount_rule" never triggers (impossible condition)
- "premium_calc" references undefined attribute "base_rate"
Quick Actions
The AI assistant provides instant access to common operations:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Create Rule | Generate rules from natural language descriptions |
| Explain Rule | Get plain-English explanation of any rule |
| Analyze Impact | See what’s affected by changes |
| Optimize | Get suggestions for improvement |
AI Capabilities
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Natural Language Processing | Understands business requirements in plain English |
| JSON Logic Generation | Converts descriptions to executable JSON Logic expressions |
| Context Awareness | Knows your product’s attributes, rules, and dependencies |
| DAG Understanding | Explains how rules connect and execute in parallel |
| Error Detection | Identifies potential issues before they cause problems |
API Architecture
Product-FARM provides dual API support for different use cases.
REST API for Management
Full-featured REST API for product management:
Endpoints:
GET /api/products- List productsPOST /api/products- Create productGET /api/products/{id}- Get product detailsPUT /api/products/{id}- Update productDELETE /api/products/{id}- Delete productPOST /api/products/{id}/clone- Clone productPOST /api/products/{id}/activate- Activate product
Features:
- OpenAPI specification
- Query parameters for filtering
- Pagination support
- Bulk operations
gRPC API for Evaluation
High-performance gRPC API for rule evaluation:
service RuleEngine {
rpc Evaluate(EvaluateRequest) returns (EvaluateResponse);
rpc EvaluateBatch(EvaluateBatchRequest) returns (EvaluateBatchResponse);
rpc EvaluateStream(stream EvaluateRequest) returns (stream EvaluateResponse);
}
message EvaluateRequest {
string product_id = 1;
map<string, Value> inputs = 2;
repeated string requested_outputs = 3;
}
Benefits:
- Binary protocol (efficient serialization)
- HTTP/2 multiplexing
- Streaming support
- Strong typing
Batch Processing
Evaluate multiple input sets in a single request:
POST /api/products/{id}/evaluate/batch
{
"inputs": [
{"age": 25, "income": 50000},
{"age": 35, "income": 75000},
{"age": 45, "income": 100000}
],
"outputs": ["premium", "risk_score"]
}
Streaming Support
Real-time evaluation with streaming:
const stream = client.evaluateStream();
stream.on('data', (response) => {
console.log('Result:', response.outputs);
});
// Send inputs as they arrive
dataSource.on('record', (record) => {
stream.write({ product_id: 'insurance', inputs: record });
});
Next Steps
- Benchmarks - Detailed performance data
- API Reference - Complete API documentation
- Architecture - System design deep-dive
- Quick Start - Get started in 5 minutes